Peer Teaching Strategies
Peer Teaching Strategies is an innovative educational approach that empowers students to take an active role in their learning by teaching their peers. This method not only enhances understanding of the subject matter but also fosters collaboration, communication, and critical thinking skills among students. In this article, we will explore various peer teaching strategies, provide examples, and discuss their benefits in the classroom.
What is Peer Teaching?
Peer teaching involves students teaching each other under the guidance of a teacher or facilitator. This collaborative learning technique allows students to engage with the material actively, reinforcing their understanding while helping others learn. The process typically includes preparation, execution, and reflection, ensuring that both the teacher and students benefit from the experience.
Benefits of Peer Teaching
- Enhanced Understanding: Teaching others helps students solidify their knowledge and identify gaps in their understanding.
- Improved Communication Skills: Explaining concepts to peers enhances verbal communication and presentation skills.
- Increased Engagement: Students are more likely to participate actively when they are involved in teaching.
- Development of Critical Thinking: Peer teaching encourages students to think critically about the material and how to convey it effectively.
- Fostering Collaboration: Working together promotes teamwork and social skills.
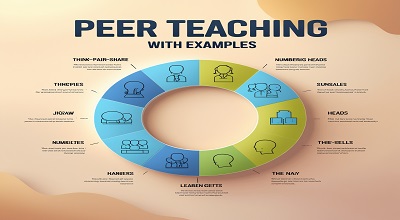
Effective Peer Teaching Strategies
1. Think, Pair, Share
Description: This strategy involves students thinking about a question or topic individually, then pairing up to discuss their thoughts before sharing with the larger group.Example: After a lecture on climate change, students take a few minutes to think about the causes and effects. They then pair up to discuss their ideas before sharing with the class.
2. Peer Tutoring
Description: In this approach, a more knowledgeable student (the tutor) helps a less knowledgeable student (the tutee) understand a specific topic.Example: A student who excels in mathematics tutors a classmate struggling with algebra concepts, providing personalized explanations and practice problems.
3. Jigsaw Method
Description: In the jigsaw method, each student becomes an expert on a specific part of a topic and then teaches that part to their peers.Example: In a history class, each student researches a different event from World War II. They then come together in groups to teach each other about their respective events, creating a comprehensive understanding of the war.
4. Group Projects
Description: Students work in small groups to complete a project, with each member responsible for a specific aspect of the work.Example: In a science class, students collaborate on a project about ecosystems, with each student researching a different ecosystem type and presenting their findings to the group.
5. Peer Review
Description: Students review each other’s work, providing constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement.Example: In a writing class, students exchange essays and provide feedback on structure, clarity, and argument strength, helping each other refine their writing skills.
6. Role-Playing
Description: Students take on different roles to explore a topic or scenario, enhancing understanding through experiential learning.Example: In a literature class, students role-play characters from a novel, discussing their motivations and actions, which deepens their comprehension of the text.
7. Teach-Back Method
Description: After learning a new concept, students explain it back to the teacher or their peers, demonstrating their understanding.Example: After a lesson on the water cycle, students explain the process to a partner, using diagrams to illustrate their points.
8. Collaborative Learning Stations
Description: Set up different stations around the classroom, each focusing on a specific topic or skill. Students rotate through the stations, teaching and learning from each other.Example: In a language class, stations could include vocabulary games, grammar exercises, and conversation practice, with students teaching each other at each station.
9. Fishbowl Discussions
Description: A small group of students discusses a topic in the center of the classroom while the rest of the class observes. Afterward, the observers can provide feedback or join the discussion.Example: In a social studies class, a group discusses the implications of a historical event while the rest of the class listens and later contributes their thoughts.
10. Concept Mapping
Description: Students create visual representations of their understanding of a topic, which they then explain to their peers.Example: After studying ecosystems, students create concept maps showing the relationships between different organisms and their environments, explaining their maps to classmates.
Implementing Peer Teaching in the Classroom
Preparation
- Select Topics: Choose topics that lend themselves well to peer teaching, ensuring they are appropriate for the students’ skill levels.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what you want students to achieve through peer teaching.
- Model the Process: Demonstrate how peer teaching works, including how to give and receive feedback.
Execution
- Group Formation: Organize students into pairs or small groups, considering their strengths and weaknesses.
- Provide Resources: Ensure students have access to materials and resources needed for their teaching.
- Monitor Progress: Circulate around the classroom to observe interactions and provide support as needed.
Reflection
- Feedback Session: After the peer teaching activity, hold a class discussion to reflect on what worked well and what could be improved.
- Self-Assessment: Encourage students to assess their own performance and that of their peers.
- Adjust Future Strategies: Use feedback to refine and improve future peer teaching activities.
Challenges of Peer Teaching
While peer teaching has numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that educators must address:
- Unequal Participation: Some students may dominate the teaching process while others remain passive. To mitigate this, set clear roles and responsibilities within groups.
- Varied Skill Levels: Students may have different levels of understanding, which can lead to frustration. Pairing students strategically can help balance skill levels.
- Lack of Confidence: Some students may feel uncomfortable teaching their peers. Providing training and support can help build their confidence.
Conclusion
Peer teaching is a powerful educational strategy that promotes active learning, collaboration, and critical thinking. By implementing various peer teaching strategies, educators can create a dynamic classroom environment where students take ownership of their learning. As students engage in teaching their peers, they not only reinforce their own understanding but also develop essential skills that will benefit them throughout their academic and professional lives.
FAQs
1. What is peer teaching?
Peer teaching is an educational approach where students teach each other, often under the guidance of a teacher. This method encourages collaboration and enhances understanding of the subject matter.
2. What are the benefits of peer teaching?
Peer teaching promotes enhanced understanding, improved communication skills, increased engagement, development of critical thinking, and fosters collaboration among students.
3. How can I implement peer teaching in my classroom?
To implement peer teaching, prepare by selecting appropriate topics, setting clear objectives, and modeling the process. During execution, organize students into groups, provide resources, and monitor their progress. Finally, reflect on the activity to improve future implementations.
4. What challenges might I face with peer teaching?
Challenges include unequal participation, varied skill levels among students, and lack of confidence in teaching. Address these by setting clear roles, pairing students strategically, and providing support and training.
5. Can peer teaching be used in all subjects?
Yes, peer teaching can be adapted for various subjects, including math, science, language arts, and social studies, making it a versatile strategy for enhancing student learning.