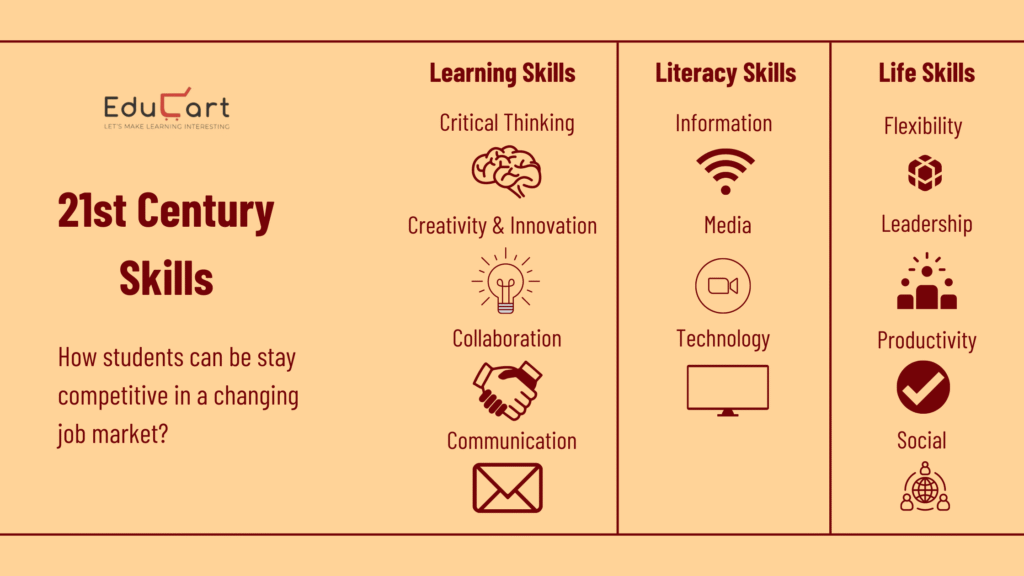
21st-Century Teaching Skills
21st-Century Teaching Skills: The education landscape has significantly transformed in the 21st century. Traditional teaching methods are being replaced by innovative approaches that emphasise critical thinking, collaboration, and adaptability. Educators are now tasked with equipping students with skills that prepare them for an ever-changing global landscape. This article delves into the essential teaching skills for the 21st century, providing real-world examples and strategies for implementation.

Critical Thinking and Problem Solving
Definition: The ability to analyze complex issues, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions.
Example: In a history class, students are presented with a controversial event. Instead of merely memorizing facts, they are tasked with researching multiple perspectives, analyzing primary sources, and presenting their findings, fostering critical analysis and debate.
Implementation Strategy: Incorporate case studies and real-world problems into the curriculum. Encourage students to question assumptions and explore various solutions.
Collaboration and Teamwork
Definition: Working effectively with others to achieve common goals.
Example: During a science project, students collaborate in groups to design an experiment, assign roles, and present their findings, emphasizing the importance of teamwork and communication.
Implementation Strategy: Organize group activities that require collective problem-solving. Assign roles within teams to ensure active participation and accountability.
Communication Skills
Definition: The ability to convey information clearly and effectively through various mediums.
Example: Students create podcasts to discuss a literary work, honing their verbal communication skills and learning to present information engagingly.
Implementation Strategy: Encourage diverse forms of communication, including presentations, written reports, and digital media. Provide constructive feedback to enhance communication proficiency.
Digital Literacy
Definition: The ability to effectively and critically navigate, evaluate, and create information using a range of digital technologies.
Example: In a digital art class, students use graphic design software to create original artwork, learning both technical skills and creative expression.
Implementation Strategy: Integrate technology into lessons, teaching students to use digital tools responsibly and creatively. Emphasize the importance of online safety and ethical digital behavior.

Adaptability and Flexibility
Definition: The capacity to adjust to new conditions and challenges.
Example: When a scheduled field trip is canceled due to weather, students quickly adapt by transitioning to a virtual tour, demonstrating flexibility in learning approaches.
Implementation Strategy: Foster a classroom environment that embraces change. Encourage students to view challenges as opportunities for growth and learning.
Creativity and Innovation
Definition: The ability to think outside the box and develop novel ideas and solutions.
Example: In a design technology class, students are tasked with creating sustainable products from recycled materials, promoting innovative thinking and environmental awareness.
Implementation Strategy: Provide open-ended projects that encourage creative problem-solving. Celebrate original ideas and approaches to learning.
Emotional Intelligence and Social Skills
Definition: The ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions, and to recognize, understand, and influence the emotions of others.
Example: Through role-playing scenarios, students practice empathy and conflict resolution, enhancing their interpersonal skills and emotional awareness.
Implementation Strategy: Incorporate activities that promote self-awareness and empathy. Create a supportive classroom environment that values emotional well-being.
Global Awareness and Cultural Competence
Definition: Understanding and appreciating cultural differences and global issues.
Example: Students engage in a project where they research and present on global environmental challenges, fostering a sense of global citizenship.
Implementation Strategy: Introduce global topics and diverse perspectives into the curriculum. Encourage discussions that promote cultural understanding and respect.
Lifelong Learning and Self-Direction
Definition: The ability to take initiative and responsibility for one’s own learning throughout life.
Example: Students set personal learning goals and track their progress, developing skills in self-motivation and time management.
Implementation Strategy: Encourage students to pursue interests beyond the standard curriculum. Provide resources and support for independent learning endeavors.
Ethical and Responsible Citizenship
Definition: Understanding and acting upon one’s responsibilities to society and the environment.
Example: Students participate in a community service project, applying classroom knowledge to address local issues and demonstrating civic responsibility.
Implementation Strategy: Integrate service learning into the curriculum. Discuss ethical dilemmas and encourage students to consider the societal impact of their actions.
Conclusion
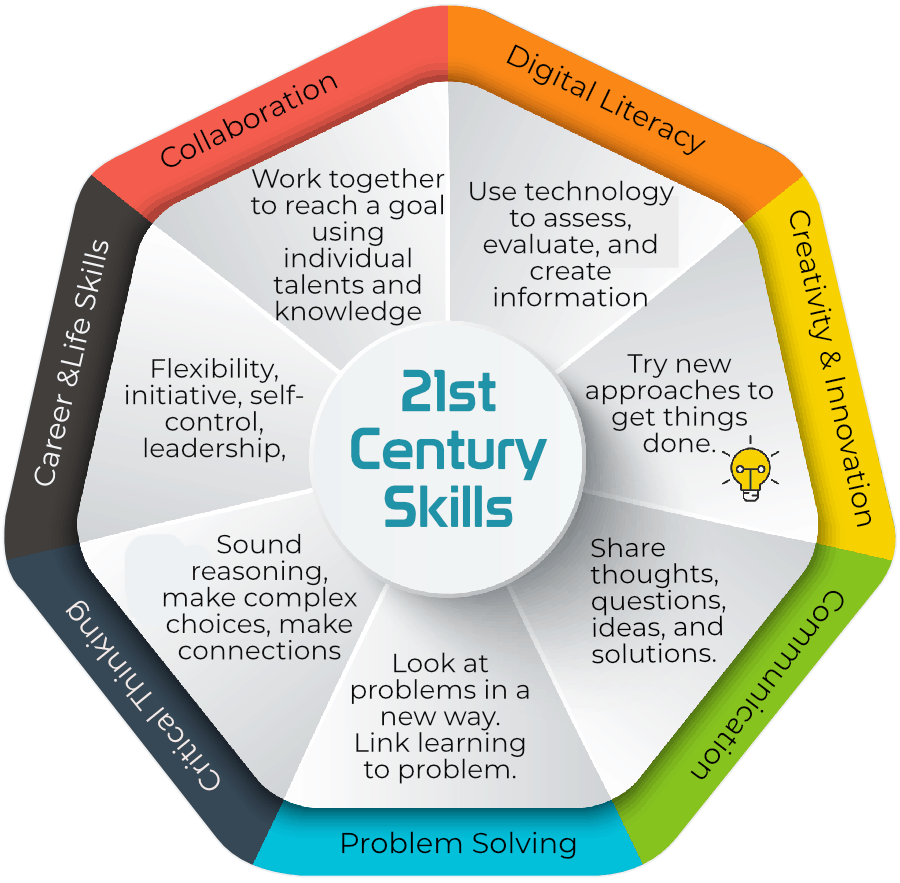
The 21st century demands a shift in educational practices to prepare students for a rapidly evolving world. By fostering skills such as critical thinking, collaboration, and digital literacy, educators can equip students with the tools necessary for success in the modern era. Implementing these skills through practical examples and strategies ensures that learning is relevant, engaging, and impactful.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the core 21st-century teaching skills?
The core skills include critical thinking, collaboration, communication, digital literacy, adaptability, creativity, emotional intelligence, global awareness, lifelong learning, and ethical citizenship.
Q2: How can I integrate technology into my teaching?
Utilize digital tools and platforms to enhance learning experiences. Incorporate online research, digital presentations, and collaborative tools to engage students.
Q3: What strategies can promote critical thinking in students?
Encourage inquiry-based learning, present real-world problems, and facilitate discussions that require analysis and evaluation of information.
Q4: How can I support students in developing emotional intelligence?
Implement activities that promote self-awareness, empathy, and social skills. Create a classroom environment that values emotional well-being and open communication.
Q5: Why is global awareness important in education?
Global awareness prepares students to understand and address international issues, fostering responsible citizenship and a broader perspective on the world.
Free Here: TF2 Mobile APK