Micro-Credentials for Teachers
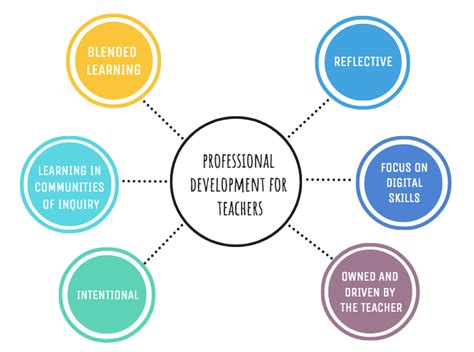
Micro-Credentials for Teachers: In the ever-evolving landscape of education, traditional professional development methods are being supplemented—and in some cases, replaced—by micro-credentials. These are short, competency-based recognitions. That allow educators to demonstrate mastery in specific areas. As the demand for personalized and flexible learning grows, micro-credentials offer a promising pathway for teachers to enhance their skills and advance their careers.

What Are Micro-Credentials?
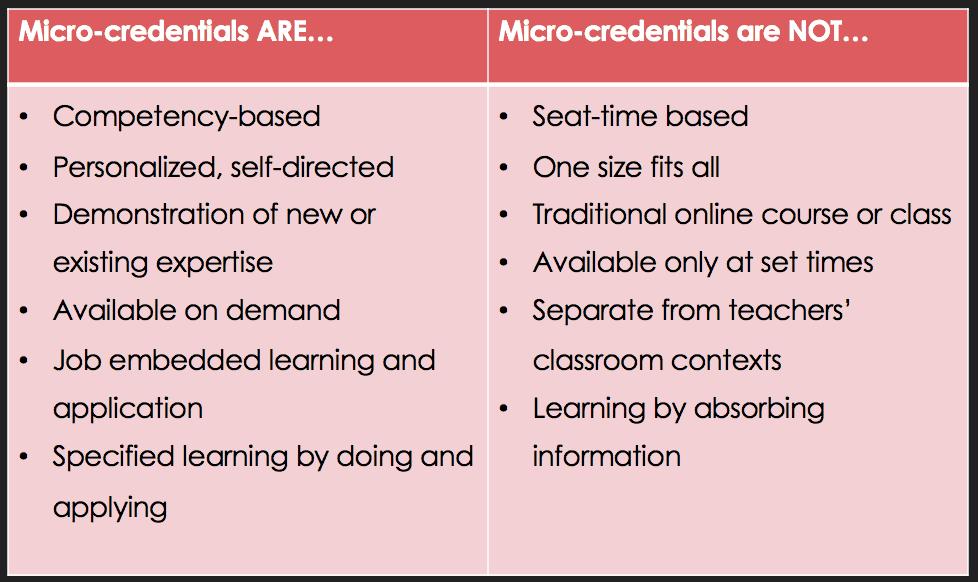
Micro-credentials are digital certifications awarded to educators who demonstrate proficiency in a particular skill or competency. Unlike traditional degrees, they are:
- Competency-Based: Teachers must provide evidence of their skills through performance tasks.
- Flexible: Educators can earn them at their own pace, often online.
- Stackable: Multiple micro-credentials can be combined to form a broader qualification.
These credentials focus on practical application, allowing teachers to immediately implement new strategies in their classrooms.
The Rise of Micro-Credentials in Education
The adoption of micro-credentials has been accelerating due to several factors:
- Personalization: Teachers can choose areas of development that align with their interests and student needs.
- Accessibility: Online platforms make it easier for educators worldwide to access these learning opportunities.
- Recognition: Institutions and employers are increasingly acknowledging micro-credentials as valid indicators of professional growth.
For instance, the National Education Association (NEA) offers over 175 micro-credentials developed by educators for educators. Covering areas like co-teaching, cultural competence, and trauma-informed practices .

Examples of Micro-Credentials for Teachers
1. Co-Teaching Micro-Credentials
These credentials focus on collaborative teaching strategies, helping educators work effectively with co-teachers to create inclusive learning environments. Topics include co-planning, co-instruction, and co-assessment .
2. Diversity, Equity, and Cultural Competence (DECC)
DECC micro-credentials aim to enhance educators’ abilities to teach diverse student populations by promoting cultural awareness and inclusive practices.
3. Trauma-Informed Pedagogy
These credentials equip teachers with strategies to support students who have experienced trauma, fostering a safe and supportive classroom environment.
4. Digital Literacy and Technology Integration
With the increasing role of technology in education, micro-credentials in digital literacy help teachers integrate tech tools effectively into their teaching practices.
5. Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)
SEL micro-credentials focus on developing educators’ skills in fostering students’ emotional intelligence and interpersonal skills.
Benefits of Micro-Credentials for Teachers
- Targeted Skill Development: Educators can focus on specific areas of improvement.
- Immediate Application: Skills learned can be applied directly in the classroom.
- Career Advancement: Earning multiple micro-credentials can lead to new opportunities and recognition.
- Flexible Learning: Teachers can learn at their own pace, balancing professional development with teaching responsibilities.
Challenges and Considerations
While micro-credentials offer numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistency and quality across different micro-credential programs.
- Recognition: Gaining widespread acceptance among educational institutions and employers.
- Integration: Aligning micro-credentials with existing professional development frameworks.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among educators, institutions, and credentialing bodies to establish standards and frameworks that ensure the effectiveness and credibility of micro-credentials.

Future Trends in Micro-Credentials
The future of micro-credentials in education looks promising:
- Increased Integration: Micro-credentials are expected to become more integrated into formal education systems.
- Employer Engagement: Employers are likely to play a more active role in recognizing and supporting micro-credentials.
- Technological Advancements: Emerging technologies will facilitate the creation and management of micro-credentials, making them more accessible and efficient.

FAQs About Micro-Credentials for Teachers
1. What is a micro-credential?
A micro-credential is a digital certification that recognizes an educator’s mastery of a specific skill or competency, typically earned through performance-based assessments.
2. How are micro-credentials different from traditional degrees?
Unlike traditional degrees, micro-credentials are focused on specific skills, are competency-based, and can be earned at an individual’s own pace, often online.
3. Are micro-credentials recognized by employers?
Recognition varies by employer and region. However, many institutions and employers are increasingly acknowledging micro-credentials as valid indicators of professional development.
4. Can micro-credentials be combined?
Yes, multiple micro-credentials can be “stacked” to demonstrate proficiency in broader areas or to meet specific career goals.
5. How can I earn a micro-credential?
Educators can earn micro-credentials through various online platforms. Such as the NEA’s Certification Bank, by completing performance tasks and submitting evidence of their competencies.
Conclusion
Micro-credentials represent a transformative approach to professional development in education. By offering personalized, flexible, and competency-based learning opportunities, they empower teachers to enhance their skills and better serve their students. As the education landscape continues to evolve, micro-credentials will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of teaching and learning.
Free Here: Rummy Palms APK
