Learning Without Limits
Learning Without Limits: In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, interdisciplinary learning has emerged as a powerful approach to fostering critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. Unlike traditional subject-based learning, interdisciplinary education integrates knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines, encouraging students to make meaningful connections across subjects.
At TeacherEducator.com, we believe in a hands-on approach to interdisciplinary learning—one that engages students in real-world applications, collaborative projects, and experiential activities. This blog post explores the latest strategies, benefits, and practical implementations of interdisciplinary learning in modern classrooms.
What Is Interdisciplinary Learning?
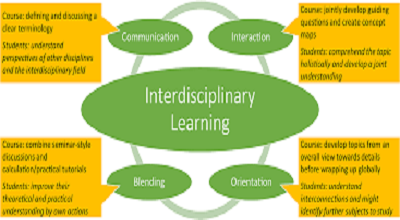
Interdisciplinary learning is an educational approach that integrates concepts, theories, and methodologies from multiple disciplines to explore complex topics. Instead of teaching subjects in isolation, educators design lessons that connect science, math, arts, social studies, and language arts, allowing students to see the bigger picture.
Key Characteristics of Interdisciplinary Learning:
- Holistic Understanding: Students explore topics from multiple perspectives.
- Problem-Centered Learning: Focuses on real-world issues rather than isolated subjects.
- Collaboration: Encourages teamwork among students and teachers.
- Critical Thinking: Prompts students to analyze and synthesize information.
Why Is Interdisciplinary Learning Important?
The modern workforce demands individuals who can think critically, adapt, and solve complex problems—skills that interdisciplinary learning nurtures. Here’s why it’s essential:
Benefits of Interdisciplinary Learning:
✅ Enhances Engagement: Students find learning more meaningful when subjects are connected to real-life scenarios.
✅ Develops Critical Thinking: Encourages analysis, evaluation, and synthesis of information.
✅ Prepares for Future Careers: Many professions require knowledge across multiple fields.
✅ Promotes Creativity: Blending different disciplines fosters innovation.
Key Principles of a Hands-On Interdisciplinary Approach
A hands-on approach makes interdisciplinary learning more engaging and effective. Here are the core principles:
a) Experiential Learning
- Students learn by doing—through experiments, field trips, and simulations.
- Example: Combining biology and environmental science by creating a school garden.
b) Project-Based Learning (PBL)
- Students work on extended projects that require research, collaboration, and presentation.
- Example: Designing a sustainable city (integrating math, science, and social studies).
c) Collaborative Teaching
- Teachers from different subjects co-plan and co-teach lessons.
- Example: A history and literature teacher collaborating on a unit about the Civil Rights Movement.
Strategies for Implementing Interdisciplinary Learning
To successfully integrate interdisciplinary learning, educators can use the following strategies:
a) Thematic Units
- Choose a central theme (e.g., “Sustainability”) and explore it through various subjects.
- Example:
- Science: Study renewable energy.
- Math: Calculate carbon footprints.
- English: Write persuasive essays on environmental policies.
b) Cross-Curricular Projects
- Assign projects that require skills from multiple subjects.
- Example: Building a bridge (engineering, physics, and art).
c) Inquiry-Based Learning
- Encourage students to ask questions and research across disciplines.
- Example: Investigating the science and history of pandemics.
Real-World Examples of Interdisciplinary Projects
Here are some inspiring interdisciplinary projects:
Example 1: “The Mars Colony Project”
- Subjects: Science, Math, Engineering, ELA
- Activity: Students design a sustainable Mars habitat, calculating resources, writing mission logs, and presenting their findings.
Example 2: “Financial Literacy Fair”
- Subjects: Math, Economics, Social Studies
- Activity: Students create business plans, budget simulations, and market research reports.
Challenges and Solutions in Interdisciplinary Education
While interdisciplinary learning is beneficial, it comes with challenges:
Challenges:
❌ Curriculum Constraints: Standardized tests often focus on single subjects.
❌ Teacher Collaboration: Requires time and coordination among educators.
Solutions:
✔ Flexible Scheduling: Allow longer class periods for interdisciplinary work.
✔ Professional Development: Train teachers in cross-disciplinary strategies.
The Role of Technology in Interdisciplinary Learning
Technology enhances interdisciplinary education through:
- Virtual Labs (Science & Tech)
- Coding & Robotics (Math & Engineering)
- Digital Storytelling (ELA & Arts)
Assessing Interdisciplinary Learning Outcomes
Assessment methods include:
- Portfolios (Showcasing work across subjects)
- Rubrics (Evaluating critical thinking and collaboration)
- Presentations (Demonstrating knowledge integration)
Future Trends in Interdisciplinary Education
Emerging trends include:
- AI & Personalized Learning
- Global Collaboration Projects
- STEAM (Science, Tech, Engineering, Arts, Math) Integration
FAQs About Interdisciplinary Learning
Q1: How does interdisciplinary learning differ from multidisciplinary learning?
A: Interdisciplinary learning integrates subjects into a unified approach, while multidisciplinary teaches them separately but around a common theme.
Q2: Can interdisciplinary learning work in standardized testing environments?
A: Yes, by aligning projects with core standards and using performance-based assessments.
Q3: What age group benefits most from interdisciplinary learning?
A: All ages, but it’s especially effective in middle school and high school.
Q4: How can parents support interdisciplinary learning at home?
A: Encourage project-based activities, discussions, and real-world problem-solving.
Q5: What resources help teachers implement interdisciplinary learning?
A: Online platforms like Khan Academy, project-based learning guides, and teacher collaboration tools.
Conclusion
A hands-on approach to interdisciplinary learning prepares students for the complexities of the modern world by fostering creativity, collaboration, and critical thinking. By integrating subjects, leveraging technology, and encouraging real-world applications, educators can create a dynamic and engaging learning environment.