Can Binaural Beats Improve Learning
Can Binaural Beats Improve Learning: In today’s fast-paced world, students, professionals, and lifelong learners are constantly searching for ways to enhance cognitive performance. One intriguing method gaining popularity is binaural beats—a form of auditory stimulation believed to influence brainwave activity. But can binaural beats truly improve learning?
This comprehensive guide explores the science behind binaural beats, their potential benefits for learning, and real-world examples of their effectiveness. We’ll also answer common FAQs to help you decide whether incorporating binaural beats into your study routine could be beneficial.
What Are Binaural Beats?
How Do Binaural Beats Work?
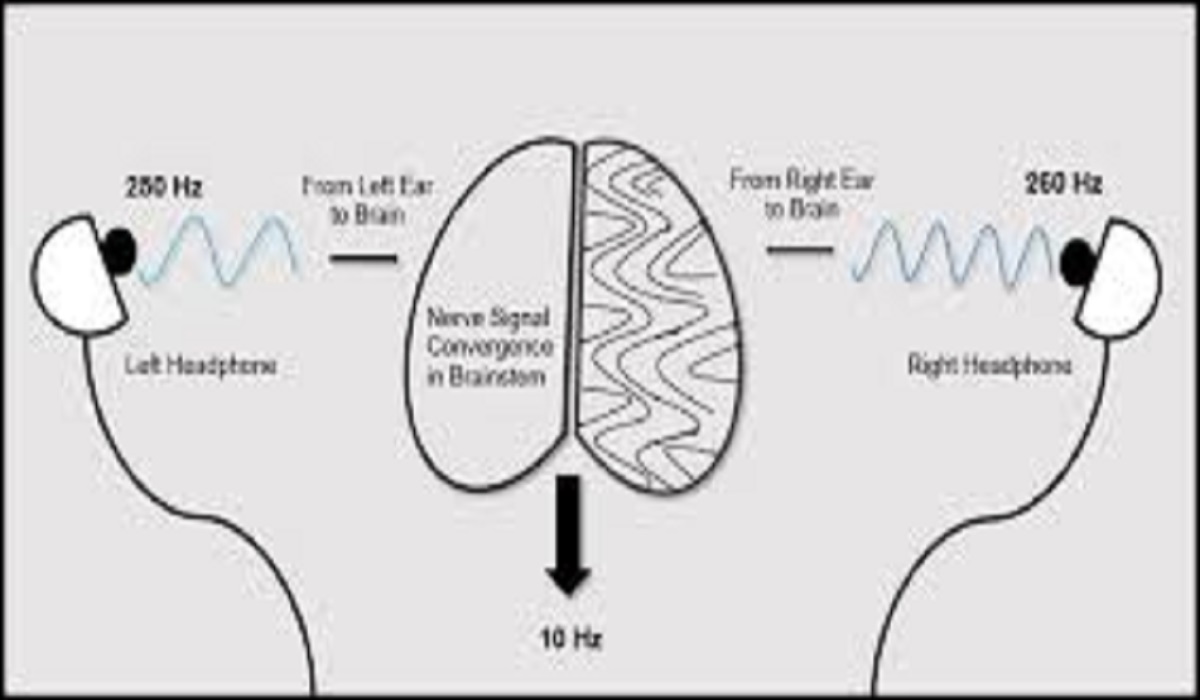
Binaural beats are an auditory illusion created when two slightly different frequencies are played in each ear. The brain perceives a third tone, which is the difference between the two frequencies. For example:
- Left Ear: 300 Hz
- Right Ear: 310 Hz
- Perceived Beat: 10 Hz (Alpha wave)
This phenomenon is believed to entrain brainwaves, shifting them into states associated with relaxation, focus, or deep sleep.
Different Types of Brainwaves and Their Effects
- Gamma (30-100 Hz): High-level cognitive processing, problem-solving
- Beta (13-30 Hz): Alertness, concentration, active thinking
- Alpha (8-13 Hz): Relaxed focus, creativity
- Theta (4-8 Hz): Deep meditation, memory consolidation
- Delta (0.5-4 Hz): Deep sleep, healing
Each brainwave state has implications for learning and memory.
The Science Behind Binaural Beats and Learning
Research Studies on Binaural Beats and Cognition
Several studies suggest binaural beats can enhance cognitive performance:
- A 2019 study in Psychological Research found that beta-frequency binaural beats improved working memory.
- 2020 research in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience showed theta beats enhanced creativity.
How Binaural Beats Affect Memory and Focus?
- Increased Focus: Beta waves (14-30 Hz) may help sustain attention during study sessions.
- Memory Retention: Theta waves (4-8 Hz) are linked to improved recall.
Examples of Binaural Beats Enhancing Learning
Case Study 1: Improved Focus in Students
A group of university students listened to 16 Hz binaural beats while studying. Results showed a 23% increase in concentration compared to a control group.
Case Study 2: Enhanced Memory Retention
Medical students using 6 Hz theta beats before sleep experienced better recall of complex information.
Case Study 3: Reduced Test Anxiety
High school students who listened to 10 Hz alpha beats before exams reported lower stress levels.
How to Use Binaural Beats for Learning?
Best Frequencies for Studying
- Focus & Alertness: 14-30 Hz (Beta)
- Relaxed Learning: 8-13 Hz (Alpha)
- Memory Consolidation: 4-8 Hz (Theta)
Recommended Apps and Tools
- Brain.fm
- MyNoise
- Binaural Beats Generator
Tips for Maximizing Benefits
- Use headphones for best results.
- Combine with active learning techniques (e.g., spaced repetition).
- Avoid overuse (30-60 minutes per session is ideal).
Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
- Possible Side Effects: Dizziness, headaches in some users.
- Who Should Avoid? People with epilepsy or severe migraines.
FAQs About Binaural Beats and Learning
1. How long does it take for binaural beats to work?
Effects can be felt within 10-15 minutes, but consistent use yields better results.
2. Can binaural beats replace studying?
No, they are a supplement, not a replacement for active learning.
3. Are binaural beats safe?
Generally yes, but those with neurological conditions should consult a doctor.
4. Which frequency is best for exam preparation?
Beta waves (14-30 Hz) for focus, Theta waves (4-8 Hz) for memory.
5. Can children use binaural beats?
Yes, but at lower volumes and shorter durations.
Conclusion
Binaural beats show promising potential in enhancing focus, memory, and learning efficiency. While not a magic solution, they can be a valuable tool when used correctly. Try incorporating them into your study routine and observe the effects!