Anti-Bias Teacher Training
Anti-Bias Teacher Training: In the ever-evolving landscape of education. Fostering an inclusive and equitable learning environment is paramount. The Anti-bias teacher training has emerged as a critical component in achieving this goal. By equipping educators with the tools and knowledge to recognize and address biases, schools can create spaces where all students feel valued and supported.
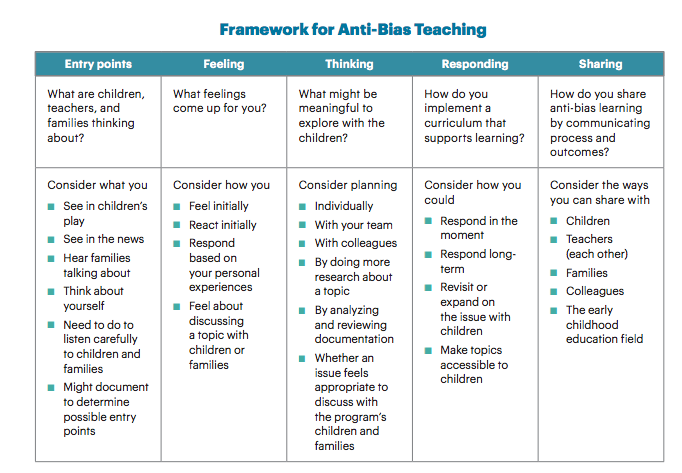
Understanding Anti-Bias Education
Anti-bias education goes beyond merely acknowledging diversity; it actively challenges prejudices, stereotypes, and discriminatory practices within the educational setting. This approach empowers teachers to create curricula and classroom environments that promote fairness and respect for all students.
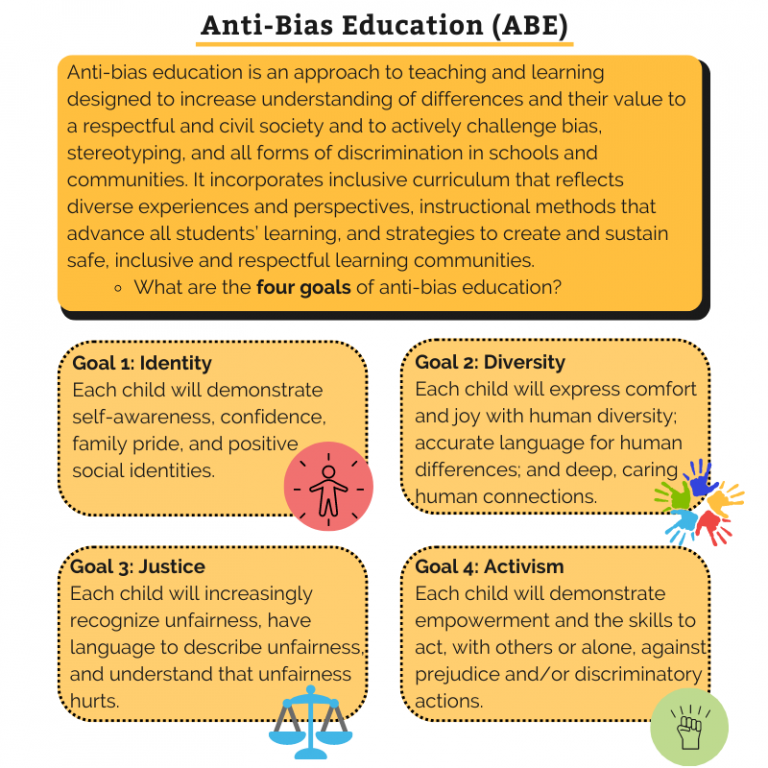
The Four Core Goals of Anti-Bias Education
- Identity: Helping children develop a strong sense of self and confidence in their abilities.
- Diversity: Encouraging appreciation and respect for differences in individuals and cultures.
- Justice: Teaching children to recognize and challenge unfairness and inequities.
- Activism: Inspiring children to take action against bias and injustice in their communities.
The Importance of Anti-Bias Training for Educators
Educators play a pivotal role in shaping the attitudes and behaviors of their students. By undergoing anti-bias training, teachers can:
- Recognize Personal Biases: Understanding their own biases allows educators to mitigate their impact on teaching.
- Create Inclusive Curricula: Designing lessons that reflect diverse perspectives ensures all students see themselves represented.
- Foster a Safe Learning Environment: Addressing discriminatory behaviors promptly promotes a culture of respect.
- Enhance Student Engagement: Students are more likely to participate in classrooms where they feel understood and valued.
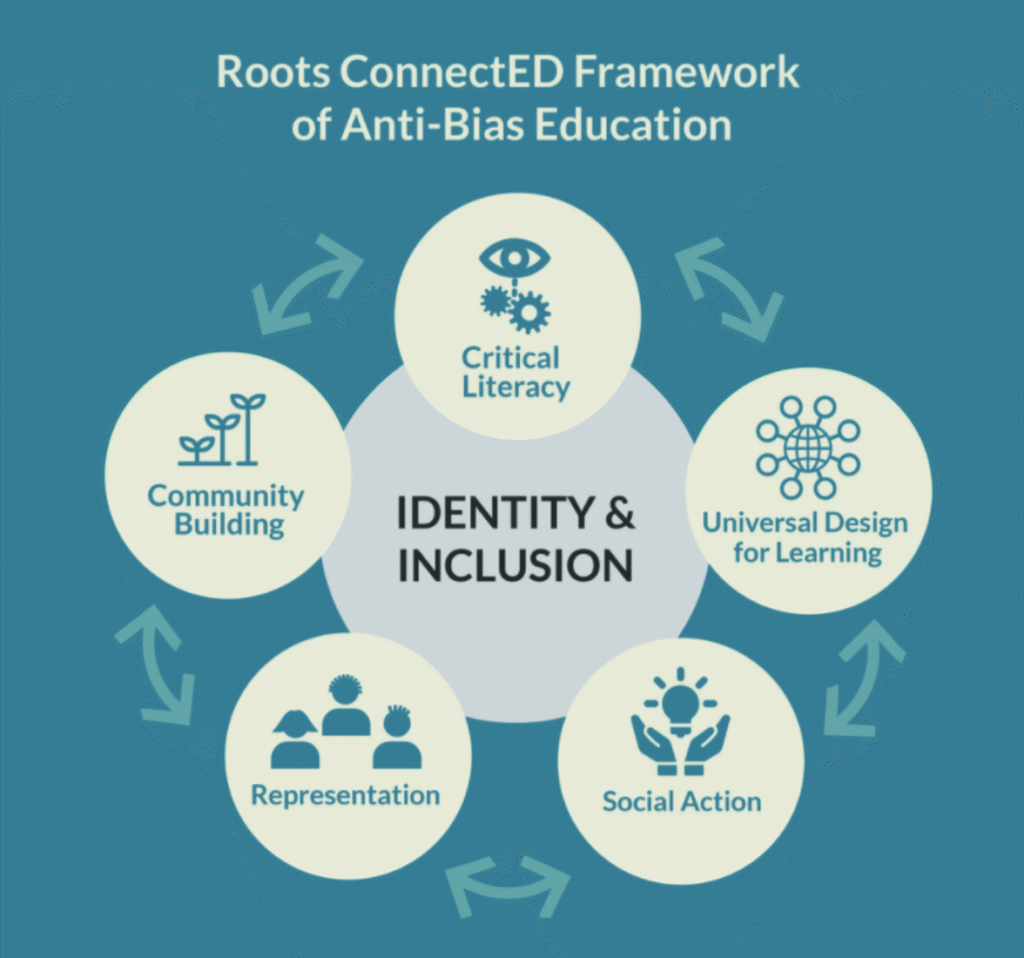
Implementing Anti-Bias Training in Schools
1. Professional Development Workshops
Regular workshops focusing on topics such as cultural competence, implicit bias, and inclusive teaching strategies can provide educators with the necessary skills and knowledge.
2. Collaborative Learning Communities
Establishing groups where teachers can share experiences, discuss challenges, and collaborate on solutions fosters a supportive environment for continuous learning.
3. Integrating Anti-Bias Concepts into the Curriculum
Incorporating themes of equity and justice into various subjects helps students understand and appreciate diversity across different contexts.
4. Engaging Families and Communities
Building partnerships with families and community members ensures that anti-bias efforts are reinforced both at school and at home.
Real-World Examples of Anti-Bias Education
Example 1: Diverse Literature in the Classroom
Incorporating books that feature characters from various backgrounds allows students to see the world through different lenses. For instance, reading stories about children from different cultures can promote empathy and understanding.
Example 2: Addressing Stereotypes Through Role-Playing
Role-playing activities where students take on different perspectives can help dismantle stereotypes and encourage critical thinking about societal norms.
Example 3: Celebrating Cultural Events
Organizing events that celebrate various cultures, such as international food days or cultural heritage months, fosters an appreciation for diversity.
Challenges in Anti-Bias Education
While the benefits are clear, implementing anti-bias education comes with challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Some educators may be hesitant to alter established practices.
- Limited Resources: Schools may lack materials or training programs focused on anti-bias education.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Navigating discussions around sensitive topics requires careful consideration and respect for all perspectives.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
- Provide Ongoing Support: Continuous professional development and resources can help educators feel confident in implementing anti-bias strategies.
- Encourage Open Dialogue: Creating safe spaces for discussions allows teachers to express concerns and share experiences.
- Utilize Diverse Resources: Leveraging a variety of materials, including literature, media, and guest speakers, enriches the learning experience.
The Role of Policy in Supporting Anti-Bias Education
Educational policies play a crucial role in promoting anti-bias education:
- Curriculum Standards: Mandating the inclusion of diversity and equity topics ensures that all students receive a comprehensive education.
- Teacher Training Requirements: Requiring anti-bias training for educators ensures that they are equipped to handle diverse classrooms.
- Accountability Measures: Implementing assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of anti-bias initiatives holds schools accountable for progress.
Future Directions in Anti-Bias Education
Looking ahead, the focus of anti-bias education is shifting towards:
- Technology Integration: Utilizing digital platforms to provide interactive and engaging anti-bias content.
- Global Perspectives: Expanding the scope of anti-bias education to include global issues and perspectives.
- Student-Led Initiatives: Empowering students to take active roles in promoting inclusivity within their schools and communities.

Conclusion
Anti-bias teacher training is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires commitment and reflection. By continuously engaging in anti-bias education, educators can create learning environments where all students feel respected, valued, and empowered to succeed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary goal of anti-bias education?
The primary goal is to create an inclusive learning environment where all students feel valued and respected, and where biases and prejudices are actively challenged.
2. How can teachers identify their own biases?
Teachers can engage in self-reflection, participate in bias assessments, and seek feedback from peers to become aware of their own biases.
3. What are some effective strategies for teaching anti-bias concepts?
Effective strategies include using diverse literature, facilitating open discussions, incorporating role-playing activities, and celebrating cultural events.
4. How can schools support anti-bias education initiatives?
Schools can support by providing professional development opportunities, integrating anti-bias content into curricula, and fostering partnerships with families and communities.
5. Why is anti-bias education important for students?
Anti-bias education helps students develop empathy, critical thinking skills, and a sense of justice, preparing them to contribute positively to a diverse society.
Free Link: Brutal Strike MOD APK
