Distributed Leadership in Schools
Distributed leadership in schools represents a transformative shift from traditional, hierarchical models to collaborative, shared leadership structures. This approach decentralizes decision-making, empowering educators at all levels to contribute to leadership processes. By fostering a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility. Distributed leadership aims to enhance educational outcomes and create a more inclusive and adaptive school environment.
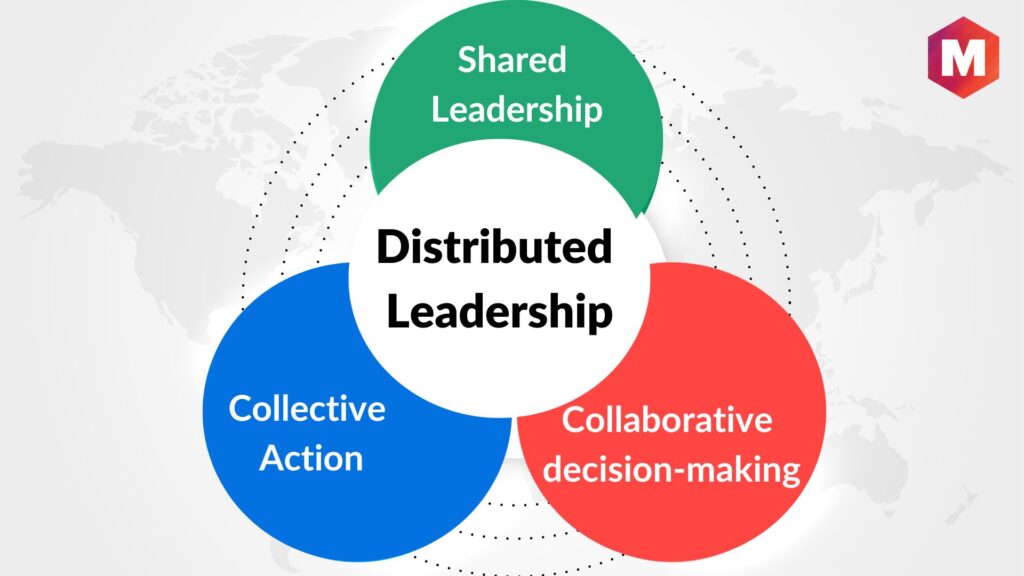
Understanding Distributed Leadership
At its core, distributed leadership involves the distribution of leadership responsibilities across various individuals within a school. Rather than being concentrated in a single leader. This model recognizes that leadership is a collective activity that emerges from the interactions among individuals, roles, and contexts within the school community.
Key Characteristics of Distributed Leadership
- Shared Responsibility: Leadership tasks and decisions are shared among teachers, administrators, and other staff members. Promoting a sense of collective ownership and accountability.
- Collaborative Decision-Making: Decisions are made through collaborative processes. Often involving teams such as grade-level groups, subject departments, or professional learning communities.
- Empowerment of Teachers: Teachers are empowered to take on leadership roles. Contributing their expertise to school improvement initiatives and fostering a culture of continuous professional development.
- Focus on Student Learning: The ultimate goal of distributed leadership is to improve student outcomes by aligning leadership efforts with instructional practices and student needs.
Theoretical Foundations
Distributed leadership draws from various educational leadership theories, including:
- Instructional Leadership: Emphasizes the role of leaders in shaping and supporting effective teaching and learning practices.
- Transformational Leadership: Focuses on inspiring and motivating staff to achieve a shared vision and foster organizational change.
- Shared Leadership: Highlights the importance of collective leadership and the distribution of influence across the organization.
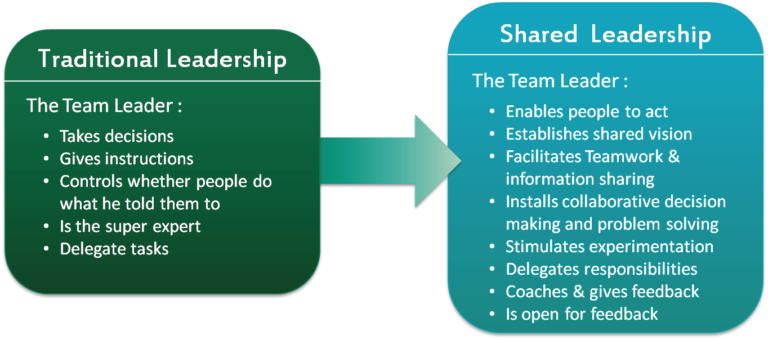
Implementing Distributed Leadership in Schools
Effective implementation of distributed leadership requires careful planning and consideration of several factors:
- Establishing Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly defined roles help ensure that leadership tasks are appropriately distributed and that all members understand their contributions to the leadership process.
- Building a Collaborative Culture: Fostering a culture of trust, open communication, and mutual respect is essential for successful collaboration among staff members.
- Providing Professional Development: Ongoing professional development opportunities equip staff with the skills and knowledge necessary to take on leadership roles effectively.
- Utilizing Data for Decision-Making: Data-driven decision-making ensures that leadership efforts are aligned with student needs and school goals.
Case Studies and Examples
- Professional Learning Communities (PLCs): Many schools have implemented PLCs. Where educators collaborate regularly to discuss student work. Share instructional strategies, and engage in collective problem-solving. This collaborative approach has been shown to improve teaching practices and student achievement.
- Instructional Leadership Teams: Some schools have established teams composed of teacher leaders, assistant principals. Other staff members who share leadership responsibilities related to curriculum development, assessment, and professional development. These teams work together to align instructional practices with school improvement goals.
- Distributed Leadership in Action: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many schools adopted distributed leadership models to respond to the challenges of remote learning. Teachers took on leadership roles in developing online curricula. Supporting students and families, and implementing new technologies, demonstrating the adaptability and effectiveness of distributed leadership in crisis situations.

Benefits of Distributed Leadership
- Enhanced Teacher Engagement: Teachers who are involved in leadership activities often experience increased job satisfaction and a stronger sense of professional identity.
- Improved Student Outcomes: By aligning leadership efforts with instructional practices, distributed leadership can lead to improved student learning and achievement.
- Sustainable School Improvement: Distributed leadership promotes a culture of continuous improvement. Making it more likely that positive changes will be sustained over time.
- Resilience and Adaptability: Schools with distributed leadership structures are better equipped to adapt to changes and challenges. As leadership is not dependent on a single individual.
Challenges and Considerations
While distributed leadership offers numerous benefits, its implementation can present challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Some staff members may be accustomed to traditional hierarchical structures and may resist the shift to a more collaborative leadership model.
- Uneven Distribution of Leadership: Without careful planning, leadership responsibilities may not be equitably distributed. Leading to burnout among some staff members and disengagement among others.
- Need for Ongoing Support: Continuous professional development and support are essential to ensure that all staff members are prepared to take on leadership roles effectively.
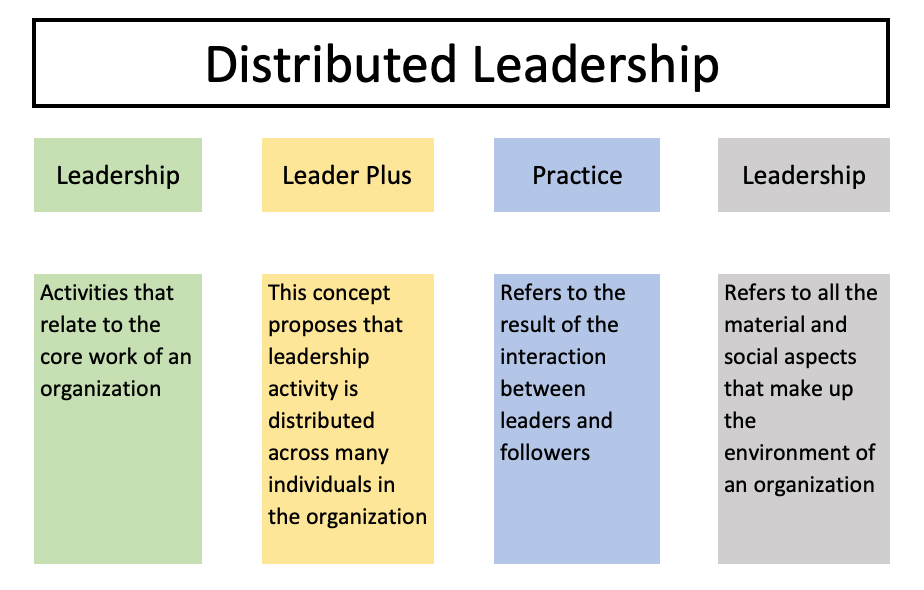
Future Directions
As educational landscapes continue to evolve, distributed leadership is likely to play an increasingly important role in school improvement efforts:
- Integration of Technology: The use of digital tools can facilitate collaboration and communication among distributed leadership teams, enhancing their effectiveness.
- Focus on Equity: Distributed leadership can help address issues of equity by involving a diverse range of voices in decision-making processes.
- Global Collaboration: Schools around the world can learn from each other’s experiences with distributed leadership, fostering a global community of practice.

Conclusion
Distributed leadership represents a paradigm shift in educational leadership, emphasizing collaboration, shared responsibility, and collective action. By empowering educators at all levels to take on leadership roles, schools can create a more inclusive, adaptive, and effective learning environment. While challenges exist, the benefits of distributed leadership—enhanced teacher engagement, improved student outcomes, and sustainable school improvement. Make it a compelling model for contemporary education.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What challenges might schools face when implementing distributed leadership?
Challenges can include resistance to change, uneven distribution of leadership responsibilities, and the need for ongoing professional development and support.
What is distributed leadership in schools?
Distributed leadership is a model where leadership responsibilities are shared among teachers, administrators, and other staff members, rather than being concentrated in a single leader.
How does distributed leadership improve student outcomes?
By aligning leadership efforts with instructional practices and student needs, distributed leadership can lead to more effective teaching and improved student learning.
What are the key characteristics of distributed leadership?
Key characteristics include shared responsibility, collaborative decision-making, empowerment of teachers, and a focus on student learning.
What are some examples of distributed leadership in action?
Examples include professional learning communities, instructional leadership teams, and teacher-led initiatives during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Free Here: Alien Shooter MOD APK
